
Analyzing Eccentric vs Concentric EMG Contractions
This lab explores EMG patterns during controlled knee or elbow flexion and extension, allowing students to compare how opposing muscle groups coordinate movement and maintain stability. By visualizing real-time muscle activation, learners can connect neuromuscular control concepts to practical applications in recovery, performance, and injury risk reduction.
Why Analyze
Eccentric & Concentric Contractions?
Balanced activation between muscles is crucial for protecting joints, controlling movement, and preventing injuries. When this coordination is disrupted—whether due to weakness, overcompensation, or improper neuromuscular control—it can lead to joint instability, increased strain, and a higher risk of re-injury, especially during rehabilitation. Understanding these muscle dynamics through EMG analysis helps identify imbalances, guide targeted interventions, and improve movement efficiency.

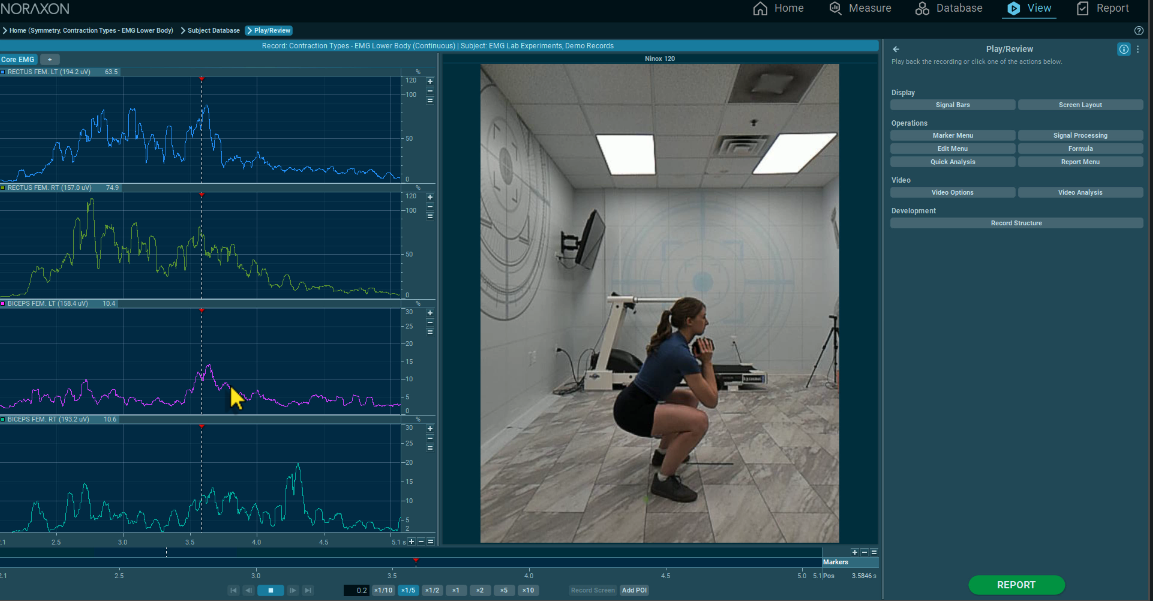
Learning Objectives for Students
Differentiate Muscle Contraction Types
-
-
Identify and define isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions.
-
Recognize when each contraction type occurs during common movements (e.g., biceps curl, squat).
-
Analyze Co-Activation for Joint Stability
-
Define co-activation and its role in enhancing joint stability during dynamic and static tasks.
-
Identify key agonist and antagonist muscle groups involved in knee and elbow movements.
Apply EMG Data to Functional Assessments
-
Use collected EMG data to compare peak activation across contraction types and loading conditions.
-
Draw conclusions on how muscle coordination and activation patterns can guide rehabilitation strategies and improve movement efficiency.


